SQL Server Database Optimization
SQL Server database optimization

The basic principle of
optimization is Benchmarking. It is a process of measuring the performance of a
product and eliminate the gaps. If an individual knows their benchmark, then
only one can try to achieve that benchmark and further improve the performance.
SQL Server database
optimization has serval options through which you can optimize the database as
well as enhance the response time of the queries.
Hello, my name is Fahad
and I have 18 years of experience working with SQL server, queries, and
optimization of DB.
During all my experience, I faced numerous challenges and problems which were regarding SQL server and query slowness. Hence, in the light of my
experience, I am humbly sharing my views on how to optimize SQL Server and SQL queries.
The following are my
considerations for the optimization of SQL Server.
1.
If you have SQL database
installed on C drive along with DB and log files on the same drive, then you
must move them to separate drives. For example, the DB must be on drive-D
whereas the log files on drive-E. This way read-write of DB will become faster,
as both the files are in separate drives, Furthermore, it is recommended that
DB should be on tap drive since it is the most efficient drive to date. you can monitor read-write on drives from Resource Monitor.
2.
Make sure there is
plenty of space on both the drives, at least 40% drives should be empty.
3.
Make sure to defragment
the devices regularly.to do defragmentation you can you windows Optimize Drives tool.
4. If the memory usage of the SQL Server is not set, it
automatically consumes all the memory and utilizes it accordingly. Therefore,
make sure to allocate 60% of the machine’s memory for the SQL server itself.
The following are my considerations for query
optimization.
1.
Try to use stored
procedures instead of plain queries in your application. Since, stored procedures
are pre-compiled; they are fast to execute and more secure, as they do not
allow SQL injection attack.
2.
If there are subqueries
in your query, then this is a performance kill and it slows down the query.
3.
Check for joins in your
queries. Removing joins can make the query more efficient.
4.
Check the query plane to identify and see if the query plan has some index scans is this is the most expensive operation in the query. you can optimize this issue by adding some non-clustered indexes.

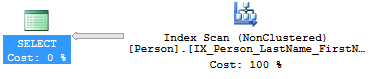

5.
Profiler reports allow
you to identify which query is making the application slow. Profiler allows you to identify
if there are any deadlocks during query execution.


6.
Cluster index allows fetching
data faster; one table can have 254 non-clustered indexes,
which allows searching data faster.
7.
Try not to use inline
functions in your queries; they work as a subquery in the background.
8.
Re-indexing your table
often is a good idea for optimization. You can have a SQL job to recreate
indexes.
Please add your comments and suggestions to make this article more informative.





Comments
Post a Comment